POI
Apache POI是基于Office Open XML标准(OOXML)和Microsoft的OLE 2复合文档格式(OLE2)处理各种文件格式的开源Java项目。 简而言之,我们可以在自己的Java程序中使用POI读写MS Excel、MS Word和MS PowerPoint文件
POI常见的使用场景
- 数据导出,如将系统中的数据导出为Excel表格
- 数据导入,如将Excel表中的信息录入到系统中(数据库)
POI结构及功能
- HSSF:提供读写MS Excel文件的功能
- XSSF:提供读写MS Excel OOXML文件的功能
- HWPF:提供读写MS Excel Word文件的功能
- HSLF:提供读写MS PowerPoint文件的功能
- HDGF:提供读写MS Visio文件的功能
POI的使用
首先需要在项目中导入相关依赖
<!--office03(xls后缀)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi</artifactId>
<version>3.9</version>
</dependency>
<!--office07(xlsx后缀)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>
<version>3.9</version>
</dependency>
<!--日期格式化工具-->
<dependency>
<groupId>joda-time</groupId>
<artifactId>joda-time</artifactId>
<version>2.10.1</version>
</dependency>
Excel文件的写入
@Test
void poiExcelWrite03() throws IOException {
//1、创建一个工作簿 07就是XSSFWorkbook
Workbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook();
//2、创建一个工作表
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("test_sheet_01");
//3、创建行和单元格,这里的0,0相当于Excel中的A,1
Row row1 = sheet.createRow(0);
Cell cell = row1.createCell(0);
//4、在单元格中写入数据
cell.setCellValue("value01");
//5、创建表文件并写入 07就是.xlsx后缀
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("E:/java_project/waston_2021/test_poi/excel/" + "test_03.xls");
workbook.write(fileOutputStream);
fileOutputStream.close();
}
在用XSSFWorkbook类对象向office07版的Excel文件写入大量数据时,会耗费较长时间,可以用SXSSFWorkbook类来解决这一问题,其原理是流式缓存
@Test
void poiExcelWriteBigData07() throws IOException {
//计时
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
Workbook workbook = new SXSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet();
//03 excel最大行数65536 07 则没有上限
for(int rowNum = 0; rowNum < 65536; rowNum++){
Row row = sheet.createRow(rowNum);
char cellChar = 'A';
for(int cellNum = 0; cellNum < 10; cellNum++){
Cell cell = row.createCell(cellNum);
cell.setCellValue(rowNum + "-" + cellChar++);
}
}
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("E:/java_project/waston_2021/test_poi/excel/" + "bigData_07.xlsx");
workbook.write(fileOutputStream);
fileOutputStream.close();
//使用SXSSFWorkbook写入会生成一个临时文件 这里清除它
((SXSSFWorkbook) workbook).dispose();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("用时" + (double)(end - begin) / 1000 + "s");
}
Excel文件的读取
@Test
void poiExcelRead07() throws IOException {
// 文件输入流
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("E:/java_project/waston_2021/test_poi/excel/" + "people.xlsx");
// 读取Excel文件中的单元格
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(fileInputStream);
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
Row row = sheet.getRow(0);
Cell cell = row.getCell(0);
//以String方式获取单元格中的值 若表中为字符 这里以getNumericCellValue获取会报错
System.out.println(cell.getStringCellValue());
fileInputStream.close();
}
对于表中数据有多种类型的解决方法
如表:
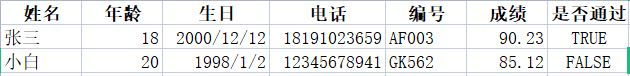
@Test
void poiComplexExcelRead07() throws IOException {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("E:/java_project/waston_2021/test_poi/excel/" + "people.xlsx");
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(fileInputStream);
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
//表的标题
Row rowTitle = sheet.getRow(0);
if(rowTitle != null){
//获取标题行的单元格数量 然后遍历
int cellCount = rowTitle.getPhysicalNumberOfCells();
for(int cellNum = 0; cellNum < cellCount; cellNum++){
Cell cell = rowTitle.getCell(cellNum);
if(cell != null){
int cellType = cell.getCellType();
String cellValue = cell.getStringCellValue();
System.out.print(cellValue + "|" );
}
}
System.out.println();
//获取表的数据行数并遍历
int rowCount = sheet.getPhysicalNumberOfRows();
for(int rowNum = 1; rowNum < rowCount; rowNum++){
Row rowData = sheet.getRow(rowNum);
if(rowData != null){
for(int cellNum = 0; cellNum < cellCount; cellNum++){
Cell cell = rowData.getCell(cellNum);
if(cell != null){
int cellType = cell.getCellType();
String cellValue = "";
//匹配数据的类型
switch (cellType){
case XSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_STRING: //字符串
System.out.print("[String]");
cellValue = cell.getStringCellValue();
break;
case XSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_BOOLEAN: //布尔
System.out.print("[Boolean]");
cellValue = String.valueOf(cell.getBooleanCellValue());
break;
case XSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_BLANK: //空
System.out.print("[Blank]");
break;
case XSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC: //数字(普通/日期)
System.out.print("[Numeric ");
//判断是否为时间
if(HSSFDateUtil.isCellDateFormatted(cell)){
System.out.print("日期]");
Date date = cell.getDateCellValue();
cellValue = new DateTime(date).toString("yyyy-MM-dd");
}else {
System.out.print("数字]");
//是数字,但为防止数字过长而报错(如电话),先转换为字符串格式
cell.setCellType(XSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_STRING);
cellValue = cell.toString();
}
break;
case XSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_ERROR: //错误
System.out.print("[Error]");
break;
}
System.out.print(cellValue);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
fileInputStream.close();
}
对于表中公式的处理,如求和公式:=SUM(B2:B4)
@Test
void poiExcelReadFormula07() throws IOException {
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("E:/java_project/waston_2021/test_poi/excel/" + "formula.xlsx");
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(inputStream);
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
Row row = sheet.getRow(4);
Cell cell = row.getCell(1);
//创建公式处理类对象
FormulaEvaluator formulaEvaluator = new XSSFFormulaEvaluator((XSSFWorkbook) workbook);
//获取单元格内容
int cellType = cell.getCellType();
if(cellType == Cell.CELL_TYPE_FORMULA){
String formula = cell.getCellFormula();
//打印公式
System.out.println(formula);
//通过公式进行计算
CellValue evaluate = formulaEvaluator.evaluate(cell);
String cellValue = evaluate.formatAsString();
System.out.println(cellValue);
}
}
EasyExcel
EasyExcel是一个基于Java的使用简单、省内存的读写Excel的开源项目。它的特点是在尽可能节约内存的情况下支持读写MS Excel (不会因Excel文件过大导致内存溢出错误)
官方网站:https://www.yuque.com/easyexcel/doc/easyexcel
使用
首先导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>easyexcel</artifactId>
<version>2.2.0-beta2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.12</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.62</version>
</dependency>
用一个Java类来映射Excel文件的一个sheet
import com.alibaba.excel.annotation.ExcelProperty;
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.Date;
@Data
@ToString
public class People {
@ExcelProperty("姓名")
private String name;
@ExcelProperty("年龄")
private int age;
@ExcelProperty("生日")
private Date birthday;
@ExcelProperty("电话")
private String phoneNum;
@ExcelProperty("编号")
private String no;
@ExcelProperty("成绩")
private double score;
@ExcelProperty("是否通过")
private Boolean isPass;
}
写入文件
import com.alibaba.excel.EasyExcel;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
class TestEasyExcelApplicationTests {
String Path = "E:/java_project/waston_2021/test_poi/excel/";
private List<People> getPeopleData(){
List<People> people = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
People p = new People();
p.setName("李四");
p.setAge(25);
p.setBirthday(new Date());
p.setNo("AB023");
p.setPhoneNum("1124568956");
p.setScore(189.6);
p.setIsPass(false);
people.add(p);
}
return people;
}
@Test
//写入文件
void easyExcelWrite() {
String fileName = Path + "EasyExcelWrite.xlsx";
//写入文件
EasyExcel.write(fileName, People.class).sheet("测试").doWrite(getPeopleData());
}
}
读取文件,需要先创建一个监听类
import com.alibaba.excel.context.AnalysisContext;
import com.alibaba.excel.event.AnalysisEventListener;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
// 有个很重要的点 DemoDataListener 不能被spring管理,要每次读取excel都要new,然后里面用到spring可以构造方法传进去
public class PeopleListener extends AnalysisEventListener<People> {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(PeopleListener.class);
/**
* 每隔5条存储数据库,实际使用中可以3000条,然后清理list ,方便内存回收
*/
private static final int BATCH_COUNT = 5;
List<People> list = new ArrayList<People>();
/**
* 假设这个是一个DAO,当然有业务逻辑这个也可以是一个service。当然如果不用存储这个对象没用。
*/
private PeopleDao peopleDao;
public PeopleListener() {
// 这里是demo,所以随便new一个。实际使用如果到了spring,请使用下面的有参构造函数
peopleDao = new PeopleDao();
}
/**
* 如果使用了spring,请使用这个构造方法。每次创建Listener的时候需要把spring管理的类传进来
*
* @param peopleDao
*/
public PeopleListener(PeopleDao peopleDao) {
this.peopleDao = peopleDao;
}
/**
* 这个每一条数据解析都会来调用
*
* @param data
* one row value. Is is same as {@link AnalysisContext#readRowHolder()}
* @param context
*/
@Override
public void invoke(People data, AnalysisContext context) {
LOGGER.info("解析到一条数据:{}", JSON.toJSONString(data));
list.add(data);
// 达到BATCH_COUNT了,需要去存储一次数据库,防止数据几万条数据在内存,容易OOM
if (list.size() >= BATCH_COUNT) {
saveData();
// 存储完成清理 list
list.clear();
}
}
/**
* 所有数据解析完成了 都会来调用
*
* @param context
*/
@Override
public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext context) {
// 这里也要保存数据,确保最后遗留的数据也存储到数据库
saveData();
LOGGER.info("所有数据解析完成!");
}
/**
* 加上存储数据库
*/
private void saveData() {
LOGGER.info("{}条数据,开始存储数据库!", list.size());
peopleDao.save(list);
LOGGER.info("存储数据库成功!");
}
}
测试读文件
@Test
//读取文件
void easyExcelRead(){
String fileName = Path + "people.xlsx";
EasyExcel.read(fileName, People.class, new PeopleListener()).sheet().doRead();
}
