JavaWeb
Web服务器
服务器
服务器通常进行一些被动操作,比如当用户发来请求时,服务器会对请求进行处理,并给用户以响应
访问网站时,机器为我们做的事:
- 用户在浏览器输入一个url地址,按下回车
- 计算机检查本机的host配置文件,看是否有该url中域名的映射
- 有:直接访问对应的ip地址
- 没有:去DNS服务器寻找对应的ip地址
- 计算机将服务器的响应返回给用户
Tomcat
- Tomcat是Apache 软件基金会(Apache Software Foundation)的Jakarta 项目中的一个核心项目,由Apache、Sun 和其他一些公司及个人共同开发而成。Tomcat 技术先进、性能稳定,而且免费,因而深受Java 爱好者的喜爱并得到了部分软件开发商的认可,成为目前比较流行的Web 应用服务器。
- Tomcat 服务器是一个免费的开放源代码的Web 应用服务器,属于轻量级应用服务器,在中小型系统和并发访问用户不是很多的场合下被普遍使用,是开发和调试JSP 程序的首选。
- 另外,Tomcat和IIS等Web服务器一样,具有处理HTML页面的功能,另外它还是一个Servlet和JSP容器,独立的Servlet容器是Tomcat的默认模式。不过,Tomcat处理静态HTML的能力不如Apache服务器。
Tomcat安装
- 在官网下载合适的tomcat压缩包
- 解压到合适的路径,tomcat就可以使用了,前提是机器配置好了jdk环境
- 配置环境变量(可选)
Tomcat启动与关闭
- 启动:bin目录下,点击startup.bat
- 关闭:bin目录下,点击shutdown.bat
- 测试:localhost:8080
Tomcat配置
tomcat服务器的核心配置文件是conf文件下的server.xml
文件详解如下:
- <connector port=”8080” protocol=”HTTP/1.1”…:指定了tomcat所占的端口号
- <Host name=”localhost”…:这里的localhost是对
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\host里localhost的映射 - appBase=”webapps”:网站应用存放的路径
Tomcat发布一个网络应用
-
在tomcat的webapps路径下,建立一个文件夹(如app1),在该文件夹下建立一个WEB-INF目录,WEB-INF下建立一个web.xml
-
web.xml内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd" version="4.0" metadata-complete="true"> </web-app> -
app1路径下,创建一些静态资源如:html、css、js等
-
启动tomcat,在浏览器输入localhost:8080/app1/xx,即可访问到xx资源
一个网络应用应有的结构:
-webapps
-ROOT
-app : 网站的目录名
-WEB-INF
-classes : 放.class文件
-lib : 放依赖的jar包
-web.xml : 应用配置文件
-index.html : 应用的首页
-xx.html
-static : 放静态资源的地方
-css
-js
-img
HTTP
什么是HTTP
- 超文本传输协议,本质是一个简单的请求-响应协议,通常运行在TCP协议之上
- 超文本指除文本之外,还可以传输图片、音乐、视频等不同格式的文件
- 该协议所占用的默认端口号是80
HTTPS
- 加密的,安全的HTTP
- 默认占用端口号:443
HTTP的版本
-
HTTP1.0:
客户端与服务端建立连接后,只能获得一个资源,然后断开连接
-
HTTP1.1:
客户端与服务端建立连接后,可以获得多个资源
HTTP请求
一个HTTP请求报文由请求行(request line)、请求头部(headers)、空行(blank line)和请求数据(request body)4个部分组成
-
请求行分为三个部分:请求方法、请求地址URL和HTTP协议版本,它们之间用空格分割。例如 :
GET /waston/sky.html HTTP/1.1 -
一个HTTP的请求头内容如下:
Host: localhost:8080 Connection: keep-alive Cache-Control: max-age=0 Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1 User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64)AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/80.0.3987.132 Safari/537.36 Sec-Fetch-Dest: document Accept:text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3;q=0.9 Sec-Fetch-Site: none Sec-Fetch-Mode: navigate Sec-Fetch-User: ?1 Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, br Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.9 If-None-Match: W/"2120-1598344459070" If-Modified-Since: Tue, 25 Aug 2020 08:34:19 GMT -
请求数据不在GET方法中使用,而在POST方法中使用。POST方法适用于需要客户填写表单的场合。与请求数据相关的最长使用的请求头部是Cntent-Type和Content-Length
HTTP响应
HTTP响应报文由状态行(status line)、相应头部(headers)、空行(blank line)和响应数据(response body)4个部分组成
-
状态行由3部分组成,分别为:协议版本、状态码、状态码扫描
HTTP/1.1 200 OK -
一个HTTP的响应头内容如下:
Date: Thu, 19 Nov 2020 06:48:09 GMT Accept-Ranges: bytes ETag: W/"2120-1598344459070" Last-Modified: Tue, 25 Aug 2020 08:34:19 GMT Content-Type: text/html Content-Length: 2120 -
响应数据可以是常见的html文件,也可以是各种各样类型的文件
Servlet
Java Servlet 是运行在 Web 服务器或应用服务器上的程序,它是作为来自 Web 浏览器或其他 HTTP 客户端的请求和 HTTP 服务器上的数据库或应用程序之间的中间层。
- 在代码层中Servlet是Sun公司提供的一个API接口,开发Servlet程序,只需两个步骤:
- 编写一个实现Servlet接口的类
- 把这个类部署到web服务器中
Servlet项目的建立
-
idear中新建maven工程(选择web-app预设),添加依赖如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>cn.waston</groupId> <artifactId>maven-web</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>war</packaging> <name>maven-web Maven Webapp</name> <!-- FIXME change it to the project's website --> <url>http://www.example.com</url> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <maven.compiler.source>1.7</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>1.7</maven.compiler.target> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.11</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId> <version>4.0.1</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId> <artifactId>javax.servlet.jsp-api</artifactId> <version>2.3.3</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <finalName>maven-web</finalName> <pluginManagement><!-- lock down plugins versions to avoid using Maven defaults (may be moved to parent pom) --> <plugins> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-clean-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.1.0</version> </plugin> <!-- see http://maven.apache.org/ref/current/maven-core/default-bindings.html#Plugin_bindings_for_war_packaging --> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-resources-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.0.2</version> </plugin> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.8.0</version> </plugin> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.22.1</version> </plugin> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.2.2</version> </plugin> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-install-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.5.2</version> </plugin> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-deploy-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.8.2</version> </plugin> </plugins> </pluginManagement> </build> </project> -
建立java包和resources包,并分进行标记(右键->mark directory as)
-
将web.xml文件内容,改为如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd" version="4.0" metadata-complete="true"> </web-app> -
编写一个servlet程序
package cn.waston.myservlet; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PrintWriter; /** * @Description: * @Author: Waston * @Date: 2020/11/19 18:16 */ public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { System.out.println("调用了doGet方法"); PrintWriter writer = resp.getWriter();//响应流 writer.print("Hello Servlet"); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { super.doGet(req, resp); } } -
在web.xml编写Servlet的映射
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd" version="4.0" metadata-complete="true"> <!--注册Servlet--> <servlet> <servlet-name>hello</servlet-name> <servlet-class>cn.waston.myservlet.HelloServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <!--Servlet的请求路径--> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>hello</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app> -
idear配置tomcat,选择版本、设置访问路径
-
启动tomcat,进行测试
Servlet原理
通过分析源码,可以发现,我们写servlet所继承的HttpServlet类继承自GenericServlet,而GenericServlet又继承自Servlet接口
Servlet接口的源码如下:
package javax.servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
public interface Servlet {
void init(ServletConfig var1) throws ServletException;
ServletConfig getServletConfig();
void service(ServletRequest var1, ServletResponse var2) throws ServletException, IOException;
String getServletInfo();
void destroy();
}
这5个方法,每个servlet实现类都会依次从上到下执行;我们也常把这5个方法称为servlet的声明周期
GenericServlet接口的源码如下:
package javax.servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
public abstract class GenericServlet implements Servlet, ServletConfig, Serializable {
private static final String LSTRING_FILE = "javax.servlet.LocalStrings";
private static ResourceBundle lStrings = ResourceBundle.getBundle("javax.servlet.LocalStrings");
private transient ServletConfig config;
public GenericServlet() {
}
public void destroy() {
}
public String getInitParameter(String name) {
ServletConfig sc = this.getServletConfig();
if (sc == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(lStrings.getString("err.servlet_config_not_initialized"));
} else {
return sc.getInitParameter(name);
}
}
public Enumeration<String> getInitParameterNames() {
ServletConfig sc = this.getServletConfig();
if (sc == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(lStrings.getString("err.servlet_config_not_initialized"));
} else {
return sc.getInitParameterNames();
}
}
public ServletConfig getServletConfig() {
return this.config;
}
public ServletContext getServletContext() {
ServletConfig sc = this.getServletConfig();
if (sc == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(lStrings.getString("err.servlet_config_not_initialized"));
} else {
return sc.getServletContext();
}
}
public String getServletInfo() {
return "";
}
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
this.config = config;
this.init();
}
public void init() throws ServletException {
}
public void log(String msg) {
this.getServletContext().log(this.getServletName() + ": " + msg);
}
public void log(String message, Throwable t) {
this.getServletContext().log(this.getServletName() + ": " + message, t);
}
public abstract void service(ServletRequest var1, ServletResponse var2) throws ServletException, IOException;
public String getServletName() {
ServletConfig sc = this.getServletConfig();
if (sc == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(lStrings.getString("err.servlet_config_not_initialized"));
} else {
return sc.getServletName();
}
}
}
GenericServlet类对5个方法除service方法外都进行了实现
HttpServlet类源码如下:
package javax.servlet.http;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.text.MessageFormat;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
import javax.servlet.GenericServlet;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletOutputStream;
import javax.servlet.ServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.ServletResponse;
public abstract class HttpServlet extends GenericServlet {
private static final String METHOD_DELETE = "DELETE";
private static final String METHOD_HEAD = "HEAD";
private static final String METHOD_GET = "GET";
private static final String METHOD_OPTIONS = "OPTIONS";
private static final String METHOD_POST = "POST";
private static final String METHOD_PUT = "PUT";
private static final String METHOD_TRACE = "TRACE";
private static final String HEADER_IFMODSINCE = "If-Modified-Since";
private static final String HEADER_LASTMOD = "Last-Modified";
private static final String LSTRING_FILE = "javax.servlet.http.LocalStrings";
private static ResourceBundle lStrings = ResourceBundle.getBundle("javax.servlet.http.LocalStrings");
public HttpServlet() {
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String protocol = req.getProtocol();
String msg = lStrings.getString("http.method_get_not_supported");
if (protocol.endsWith("1.1")) {
resp.sendError(405, msg);
} else {
resp.sendError(400, msg);
}
}
protected long getLastModified(HttpServletRequest req) {
return -1L;
}
protected void doHead(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
NoBodyResponse response = new NoBodyResponse(resp);
this.doGet(req, response);
response.setContentLength();
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String protocol = req.getProtocol();
String msg = lStrings.getString("http.method_post_not_supported");
if (protocol.endsWith("1.1")) {
resp.sendError(405, msg);
} else {
resp.sendError(400, msg);
}
}
protected void doPut(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String protocol = req.getProtocol();
String msg = lStrings.getString("http.method_put_not_supported");
if (protocol.endsWith("1.1")) {
resp.sendError(405, msg);
} else {
resp.sendError(400, msg);
}
}
protected void doDelete(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String protocol = req.getProtocol();
String msg = lStrings.getString("http.method_delete_not_supported");
if (protocol.endsWith("1.1")) {
resp.sendError(405, msg);
} else {
resp.sendError(400, msg);
}
}
private Method[] getAllDeclaredMethods(Class<? extends HttpServlet> c) {
Class<?> clazz = c;
Method[] allMethods;
for(allMethods = null; !clazz.equals(HttpServlet.class); clazz = clazz.getSuperclass()) {
Method[] thisMethods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
if (allMethods != null && allMethods.length > 0) {
Method[] subClassMethods = allMethods;
allMethods = new Method[thisMethods.length + allMethods.length];
System.arraycopy(thisMethods, 0, allMethods, 0, thisMethods.length);
System.arraycopy(subClassMethods, 0, allMethods, thisMethods.length, subClassMethods.length);
} else {
allMethods = thisMethods;
}
}
return allMethods != null ? allMethods : new Method[0];
}
protected void doOptions(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
Method[] methods = this.getAllDeclaredMethods(this.getClass());
boolean ALLOW_GET = false;
boolean ALLOW_HEAD = false;
boolean ALLOW_POST = false;
boolean ALLOW_PUT = false;
boolean ALLOW_DELETE = false;
boolean ALLOW_TRACE = true;
boolean ALLOW_OPTIONS = true;
for(int i = 0; i < methods.length; ++i) {
String methodName = methods[i].getName();
if (methodName.equals("doGet")) {
ALLOW_GET = true;
ALLOW_HEAD = true;
} else if (methodName.equals("doPost")) {
ALLOW_POST = true;
} else if (methodName.equals("doPut")) {
ALLOW_PUT = true;
} else if (methodName.equals("doDelete")) {
ALLOW_DELETE = true;
}
}
StringBuilder allow = new StringBuilder();
if (ALLOW_GET) {
allow.append("GET");
}
if (ALLOW_HEAD) {
if (allow.length() > 0) {
allow.append(", ");
}
allow.append("HEAD");
}
if (ALLOW_POST) {
if (allow.length() > 0) {
allow.append(", ");
}
allow.append("POST");
}
if (ALLOW_PUT) {
if (allow.length() > 0) {
allow.append(", ");
}
allow.append("PUT");
}
if (ALLOW_DELETE) {
if (allow.length() > 0) {
allow.append(", ");
}
allow.append("DELETE");
}
if (ALLOW_TRACE) {
if (allow.length() > 0) {
allow.append(", ");
}
allow.append("TRACE");
}
if (ALLOW_OPTIONS) {
if (allow.length() > 0) {
allow.append(", ");
}
allow.append("OPTIONS");
}
resp.setHeader("Allow", allow.toString());
}
protected void doTrace(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String CRLF = "\r\n";
StringBuilder buffer = (new StringBuilder("TRACE ")).append(req.getRequestURI()).append(" ").append(req.getProtocol());
Enumeration reqHeaderEnum = req.getHeaderNames();
while(reqHeaderEnum.hasMoreElements()) {
String headerName = (String)reqHeaderEnum.nextElement();
buffer.append(CRLF).append(headerName).append(": ").append(req.getHeader(headerName));
}
buffer.append(CRLF);
int responseLength = buffer.length();
resp.setContentType("message/http");
resp.setContentLength(responseLength);
ServletOutputStream out = resp.getOutputStream();
out.print(buffer.toString());
}
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String method = req.getMethod();
long lastModified;
if (method.equals("GET")) {
lastModified = this.getLastModified(req);
if (lastModified == -1L) {
this.doGet(req, resp);
} else {
long ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader("If-Modified-Since");
if (ifModifiedSince < lastModified) {
this.maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
this.doGet(req, resp);
} else {
resp.setStatus(304);
}
}
} else if (method.equals("HEAD")) {
lastModified = this.getLastModified(req);
this.maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
this.doHead(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("POST")) {
this.doPost(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("PUT")) {
this.doPut(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("DELETE")) {
this.doDelete(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("OPTIONS")) {
this.doOptions(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("TRACE")) {
this.doTrace(req, resp);
} else {
String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented");
Object[] errArgs = new Object[]{method};
errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs);
resp.sendError(501, errMsg);
}
}
private void maybeSetLastModified(HttpServletResponse resp, long lastModified) {
if (!resp.containsHeader("Last-Modified")) {
if (lastModified >= 0L) {
resp.setDateHeader("Last-Modified", lastModified);
}
}
}
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException {
if (req instanceof HttpServletRequest && res instanceof HttpServletResponse) {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest)req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse)res;
this.service(request, response);
} else {
throw new ServletException("non-HTTP request or response");
}
}
}
注意其中的service方法,它根据客户端请求的类型,去回调对应的方法,如doGet、doPost等
Servlet在容器中的执行过程:
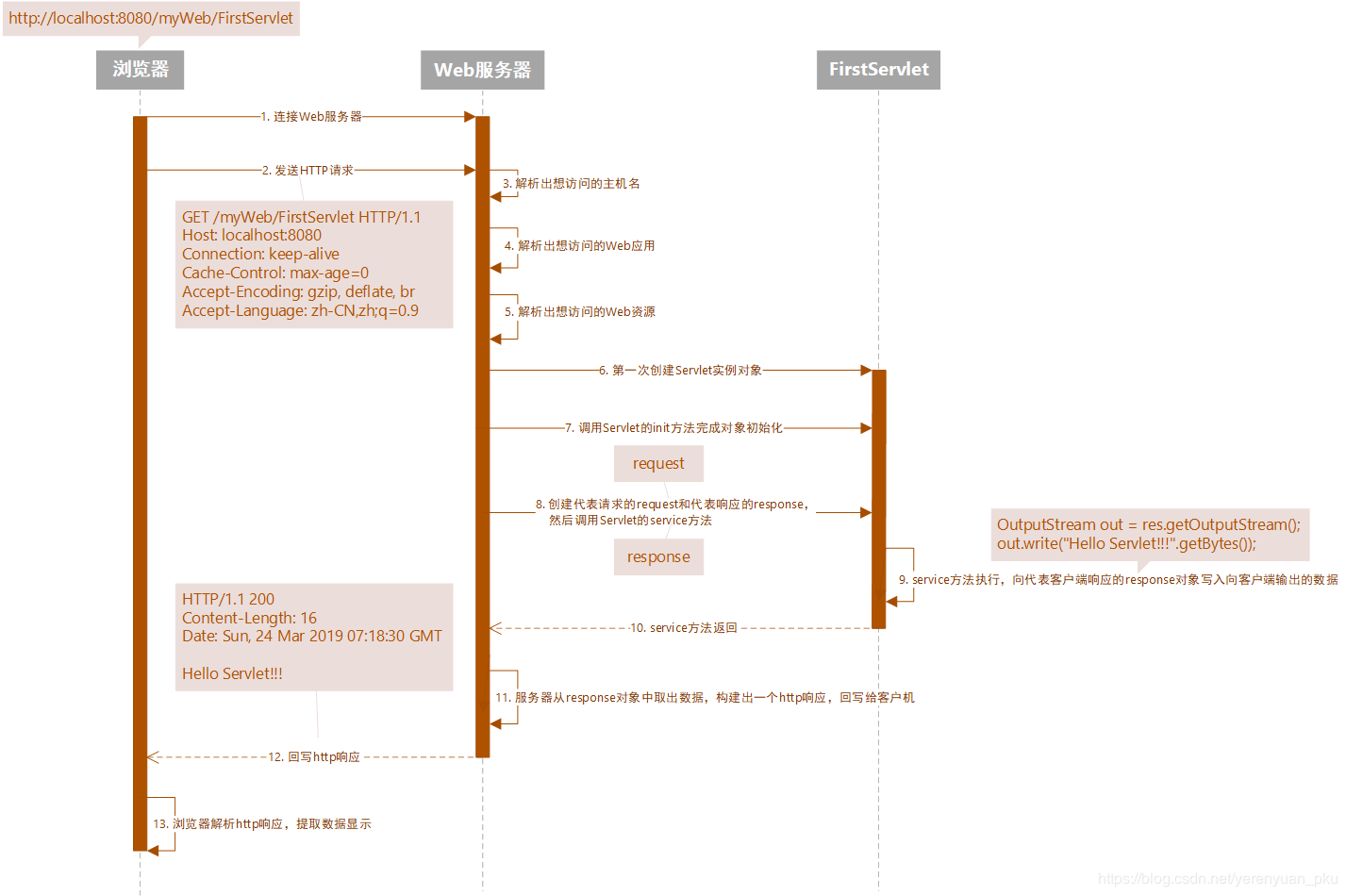
- 服务器启动时,会把我们编写的servlet类生成对象,并开始它的生命周期(执行init()方法)…
- 客户端(浏览器)在首次访问服务器(servlet容器)时,服务器会分别生成ServletRequest和ServletResponse这两个接口的实现类的一个对象
- 服务器得到url的值,根据逻辑(web.xml),开启一个线程,找到对应的servlet,执行service()方法时,把request和response作为参数传入
- service()方法执行过程中,负责向客户端响应的response对象写入向客户端输出数据
- service()方法执行完后,服务器从response对象中取出数据,构建一个http响应,返回给客户端
用时序图描述该过程如下:
- 在容器中的每个Servlet原则上只有一个实例
- 每个请求对应一个线程
- 多个线程可作用于同一个Servlet(这是造成Servlet线程不安全的根本原因)
- 每个线程一旦执行完任务,就被销毁或放在线程池中等待回收
ServletContext
Web容器在启动的时候,会为每个web程序都创建一个对应的ServletContext对象,它代表了当前的web应用
ServletContext的应用:
- 共享数据:在一个servlet中保存的数据,可以在另一个servlet中拿到
- 配置一些web应用的初始化参数
- 请求转发(请求路径不变)
- 获取项目资源文件里的内容
利用ServletContext共享数据:
-
SetServlet中调出ServletContext对象,并在放入键和值
public class SetServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { ServletContext context = this.getServletContext(); context.setAttribute("username","waston"); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { this.doGet(req, resp); } } -
GetServlet中调出ServletContext对象,获取该键的值
public class GetServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { ServletContext context = this.getServletContext(); Object username = context.getAttribute("username"); resp.setContentType("text/html"); resp.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); resp.getWriter().print("name" + username); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { this.doGet(req, resp); } }
利用ServletContext配置应用初始化:
-
web.xml中配置一些信息
<context-param> <param-name>url</param-name> <param-value>jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test</param-value> </context-param> -
servlet中通过ServletContext获取该信息
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { ServletContext context = this.getServletContext(); String url = context.getInitParameter("url"); resp.setContentType("text/html"); resp.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); resp.getWriter().print(url); }
利用ServletContext请求转发:
-
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { ServletContext context = this.getServletContext(); RequestDispatcher requestDispatcher = context.getRequestDispatcher("/hello"); requestDispatcher.forward(req, resp); }
利用ServletContext读取资源文件:
-
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { InputStream resourceAsStream = this.getServletContext().getResourceAsStream("/WEB-INF/classes/db.properties"); Properties properties = new Properties(); properties.load(resourceAsStream); String name = properties.getProperty("name"); String password = properties.getProperty("password"); resp.getWriter().print("name:" + name +",password:" + password); }
Response
当服务器接收到请求时,会生成一个继承于HttpServletResponse的对象,主要用于记录需要向客户端返回的数据
主要方法
-
负责向浏览器发送数据的方法:
ServletOutputStream getOutputStream() throws IOException; PrintWriter getWriter() throws IOException;getOutputStream() getWriter() -
负责向浏览器发送响应头的方法:
void setDateHeader(String var1, long var2); void addDateHeader(String var1, long var2); void setHeader(String var1, String var2); void addHeader(String var1, String var2); void setIntHeader(String var1, int var2); void addIntHeader(String var1, int var2);
主要应用:
- 暂存向客户端返回的数据
- 使客户端能够下载文件(资源)
- 验证码功能
- 重定向
使客户端能够下载文件:
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 获取要下载文件的路径
String realPath = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/test.png";
// 获取文件名
String fileName = realPath.substring(realPath.lastIndexOf("\\") + 1);
// 设置响应头,让浏览器实施下载、URLEncoder
resp.setHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename" + URLEncoder.encode(fileName, "UTF-8"));
// 创建下载文件的输入流
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(realPath);
// 创建缓冲区
int len = 0;
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
// 创建OutputStream对象
ServletOutputStream outputStream = resp.getOutputStream();
// 将FileOutputStream流写入到buffer缓冲区,使用OutputStream将缓冲区中的数据输出到客户端
while ((len= inputStream.read()) > 0){
outputStream.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
inputStream.close();
outputStream.close();
}
验证码功能实现:
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 使浏览器3秒刷新一次
resp.setHeader("refresh", "3");
// 创建一张图片
BufferedImage image = new BufferedImage(80, 20, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
Graphics2D graphics = (Graphics2D) image.getGraphics();
graphics.setColor(Color.white);
graphics.fillRect(0 ,0 ,80, 20);
// 在图片上写东西
graphics.setColor(Color.blue);
graphics.setFont(new Font(null, Font.BOLD, 20));
graphics.drawString(makeNum(), 0 ,20);
// 设置响应
resp.setContentType("image/jpeg");
resp.setDateHeader("expires", -1);
resp.setHeader("Cache-Control", "no-cache");
resp.setHeader("Pragma", "no-cache");
JPEGImageEncoder encoder = JPEGCodec.createJPEGEncoder(resp.getOutputStream());
encoder.encode(image);
}
//生成7位随机数
private String makeNum(){
Random random = new Random();
String num = random.nextInt(9999999) + "";
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
for(int i = 0; i < 7 - num.length(); i++){
sb.append("0");
}
num = sb.toString() + num;
return num;
}
重定向实现:
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 重定向
resp.sendRedirect("/waston/code");
}
如下这样也能达到sendRedirect的效果
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.setHeader("Location", "/waston/code");
resp.setStatus(302);
}
前后端联动:
index.jsp
<html>
<body>
<h2>Hello World!</h2>
<%--pageContext.request.contextPath代表当前项目--%>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/redirect" method="get">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username"> <br>
密码:<input type="password" name="password"> <br>
<input type="submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
servlet
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String username = req.getParameter("username");
String password = req.getParameter("password");
System.out.println(username + password);
resp.sendRedirect("/waston/success.jsp");
}
success.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>成功</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Success!</h1>
</body>
</html>
Request
当服务器接收到请求时,会生成一个继承于HttpServletRequest的对象,主要用于从客户端的请求中获取一些数据
主要应用:
-
根据参数名获取前端传过来的参数值
//username与前端元素的name值相对应 String username = req.getParameter("username"); //获取多个值,如复选框中的值 String[] items = req.getParameterValues("items"); -
请求转发
req.getRequestDispatcher("success.jsp").forward(req, resp);
Session
Session的翻译为会话
- 会话:用户打开浏览器,访问一些web资源,提交一些表单,然后关闭浏览器,这一过程称之为“会话”
- 会话状态:服务端与客户端在会话过程中产生的状态信息,借助会话状态,服务端能够把属于同一会话中的一系列的请求和响应过程关联起来
- 在Servlet规范中,常用Cookie和Session两种机制完成会话跟踪 ,以实现有状态的会话
- 服务器会为每一个客户端自动创建一个seesion,并创建一个name为JSESSIONID,value为id值的cookie给客户端;客户端再次访问该应用时,会把这个cookie带上
Session的应用:
- 客户端在切换某一应用的不同页面或不同站点时,登陆信息在服务端保存;用户不用频繁登陆、验证
- 不同servlet之间共享信息,根ServletContext类似
测试Session:
-
Session1Servlet.java
public class Session1Servlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); resp.setHeader("content-type", "text/html;charset=UTF-8"); resp.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); //从request对象中获取session HttpSession session = req.getSession(); //session中存东西 session.setAttribute("name", "waston"); } } -
Session2Servlet.java
public class Session2Servlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); resp.setHeader("content-type", "text/html;charset=UTF-8"); resp.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); //从request对象中获取session HttpSession session = req.getSession(); //从session中 String name = (String) session.getAttribute("name"); System.out.println(name); String id = session.getId(); //判断session是不是新生成的 if(session.isNew()){ resp.getWriter().write("session创建成功,id:" + id); } else { resp.getWriter().write("session已在服务器中存在,id:" + id); } } } -
在浏览器先后访问1、2两个servlet,在控制台可以看到在1中存入的信息;在浏览器看到JSESSIONID的id
Session的其他方法:
// 移除session的属性
session.removeAttribute("name");
// session注销
session.invalidate();
web.xml中设置session:
<!--设置session的存活时间为15分钟-->
<session-config>
<session-timeout>15</session-timeout>
</session-config>
Cookie
客户端在首次访问服务端时,服务端给客户端一个cookie;下次客户端访问时带着cookie,服务端看到了cookie,会省去一些验证,让客户端更快速的访问自己的资源
Cookie的使用:
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
resp.setHeader("content-type", "text/html;charset=UTF-8");
resp.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
PrintWriter out = resp.getWriter();
// 通过request对象获得cookie,cookie可以是多个
Cookie[] cookies = req.getCookies();
if(cookies != null){
for(Cookie cookie : cookies){
if(cookie.getName().equals("lastLoginTime")){
long lastLoginTime = Long.parseLong(cookie.getValue());
Date date = new Date(lastLoginTime);
out.write("您上次的访问时间是:" + date.toLocaleString());
}
}
}else {
out.write("这是您第一次访问");
}
//给客户端一个cookie
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("lastLoginTime", System.currentTimeMillis() + "");
resp.addCookie(cookie);
}
cookie设置保存时间(有效期):
//设置cookie有效期为1天 关闭浏览器后cookie还在
cookie.setMaxAge(24*60*60);
- 若不设置有效期,关闭浏览器,cookie即失效
- 若参数为0,则响应完成后,cookie立即失效
cookie特点:
- 一个Cookie只能保存一个信息
- 一个web应用可以给客户端发送多个cookie,最多为20个
- 浏览器可能最多支持存放300个cookie
- 一个cookie内容不能超过4kb
Session与Cookie的联系与区别
- Cookie和Session两种机制都用于完成会话跟踪 ,以实现有状态的会话
- Cookie是把用户的数据写给用户的浏览器,由浏览器保存
- Session是把用户的数据写到用户独占的Session中,在服务端保存;客户端则保存cookie形式的Session的id
- Cookie可以保存多个;Session只有一个,一般用于保存重要信息
